 Graphic designers create visual concepts, using computer software or by hand, to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, and captivate consumers. They develop the overall layout and production design for applications such as advertisements, brochures, magazines, and reports.
Graphic designers create visual concepts, using computer software or by hand, to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, and captivate consumers. They develop the overall layout and production design for applications such as advertisements, brochures, magazines, and reports.
Duties
Graphic designers typically do the following:
- Meet with clients or the art director to determine the scope of a project
- Use digital illustration, photo editing software, and layout software to create designs
- Create visual elements such as logos, original images, and illustrations to help deliver a message
- Design layouts, including selection of colors, images, and typefaces
- Present design concepts to clients or art directors
- Incorporate changes recommended by clients or art directors into final designs
- Review designs for errors before printing or publishing them
Graphic designers, also referred to as graphic artists or communication designers, combine art and technology to communicate ideas through images and the layout of websites and printed pages. They may use a variety of design elements to achieve artistic or decorative effects.
Graphic designers work with both text and images. They often select the type, font, size, color, and line length of headlines, headings, and text. Graphic designers also decide how images and text will go together in print or on a webpage, including how much space each will have. When using text in layouts, graphic designers collaborate with writers, who choose the words and decide whether the words will be put into paragraphs, lists, or tables. Through the use of images, text, and color, graphic designers may transform data into visual graphics and diagrams to make complex ideas more accessible.
Graphic design is important to market and sell products, and it is a critical component of brochures and logos. Therefore, graphic designers often work closely with people in advertising and promotions, public relations, and marketing.
Frequently, designers specialize in a particular category or type of client. For example, some designers create the graphics used on product packaging, and others may work on the visual designs used on book jackets.
Graphic designers need to keep up to date with software and computer technologies in order to remain competitive.
Some individuals with a background in graphic design become postsecondary teachers and teach in design schools, colleges, and universities.
Some graphic designers specialize in experiential graphic design. These designers work with architects, industrial designers, landscape architects, and interior designers to create interactive design environments, such as museum exhibitions, public arts exhibits, and retail spaces.
Education for Graphic Designers
A bachelor’s degree in graphic design or a related field is usually required. However, individuals with a bachelor’s degree in another field may pursue technical training in graphic design to meet most hiring qualifications.
The National Association of Schools of Art and Design accredits about 350 postsecondary colleges, universities, and independent institutes with programs in art and design. Most programs include courses in studio art, principles of design, computerized design, commercial graphics production, printing techniques, and website design. In addition, students should consider courses in writing, marketing, and business, all of which are useful in helping designers work effectively on project teams.
High school students interested in graphic design should take basic art and design courses in high school, if the courses are available. Many bachelor’s degree programs require students to complete a year of basic art and design courses before being admitted to a formal degree program. Some schools require applicants to submit sketches and other examples of their artistic ability.
Many programs provide students with the opportunity to build a professional portfolio of their designs. For many artists, including graphic designers, developing a portfolio—a collection of completed works that demonstrates their styles and abilities—is essential because employers rely heavily on a designer’s portfolio in deciding whether to hire the individual.
Graphic designers must keep up with new and updated computer graphics and design software, either on their own or through formal software training programs. Professional associations that specialize in graphic design, such as AIGA, offer courses intended to keep the skills of their members up to date.
Other Experience for Graphic Designers
Graphic designers often gain their initial experience through internships. Internships provide aspiring graphic designers an opportunity to work with designers and to experience the design process from concept to completion, in some cases while completing a design program.
Licenses, Certifications, and Registrations for Graphic Designers
Certification programs are generally available through software product vendors. Certification in graphic design software can demonstrate a level of competence and may provide a jobseeker with a competitive advantage.
Advancement for Graphic Designers
Experienced graphic designers may advance to chief designer, art director, or other supervisory positions.
Important Qualities for Graphic Designers
Analytical skills. Graphic designers must be able to look at their work from the point of view of their consumers and examine how the designs they develop will be perceived by consumers to ensure they convey the client’s desired message.
Artistic ability. Graphic designers must be able to create designs that are artistically interesting and appealing to clients and consumers. They produce rough illustrations of design ideas, either by hand sketching or by using computer programs.
Communication skills. Graphic designers must communicate with clients, customers, and other designers to ensure that their designs accurately reflect the desired message and effectively express information.
Computer skills. Most graphic designers use specialized graphic design software to prepare their designs.
Creativity. Graphic designers must be able to think of new approaches to communicating ideas to consumers. They develop unique designs that convey a certain message on behalf of their clients.
Time-management skills. Graphic designers often work on multiple projects at the same time, each with a different deadline.
Art Directors
Art directors are responsible for the visual style and images in magazines, newspapers, product packaging, and movie and television productions. They create the overall design of a project and direct others who develop artwork and layouts.
Craft and Fine Artists
Craft and fine artists use a variety of materials and techniques to create art for sale and exhibition. Craft artists create handmade objects, such as pottery, glassware, textiles, and other objects that are designed to be functional. Fine artists, including painters, sculptors, and illustrators, create original works of art for their aesthetic value, rather than for a functional one.
Desktop Publishers
Desktop publishers use computer software to design page layouts for newspapers, books, brochures, and other items that are printed or published online.
Drafters
Drafters use software to convert the designs of engineers and architects into technical drawings. Most workers specialize in architectural, civil, electrical, or mechanical drafting and use technical drawings to help design everything from microchips to skyscrapers.
Industrial Designers
Industrial designers develop the concepts for manufactured products, such as cars, home appliances, and toys. They combine art, business, and engineering to make products that people use every day. Industrial designers consider the function, aesthetics, production costs, and usability of products when developing new product concepts.
Multimedia Artists and Animators
Multimedia artists and animators create animation and visual effects for television, movies, video games, and other forms of media.
Technical Writers
Technical writers, also called technical communicators, prepare instruction manuals, how-to guides, journal articles, and other supporting documents to communicate complex and technical information more easily. They also develop, gather, and disseminate technical information through an organization’s communications channels.
Web Developers
Web developers design and create websites. They are responsible for the look of the site. They are also responsible for the site’s technical aspects, such as its performance and capacity, which are measures of a website’s speed and how much traffic the site can handle. In addition, web developers may create content for the site.
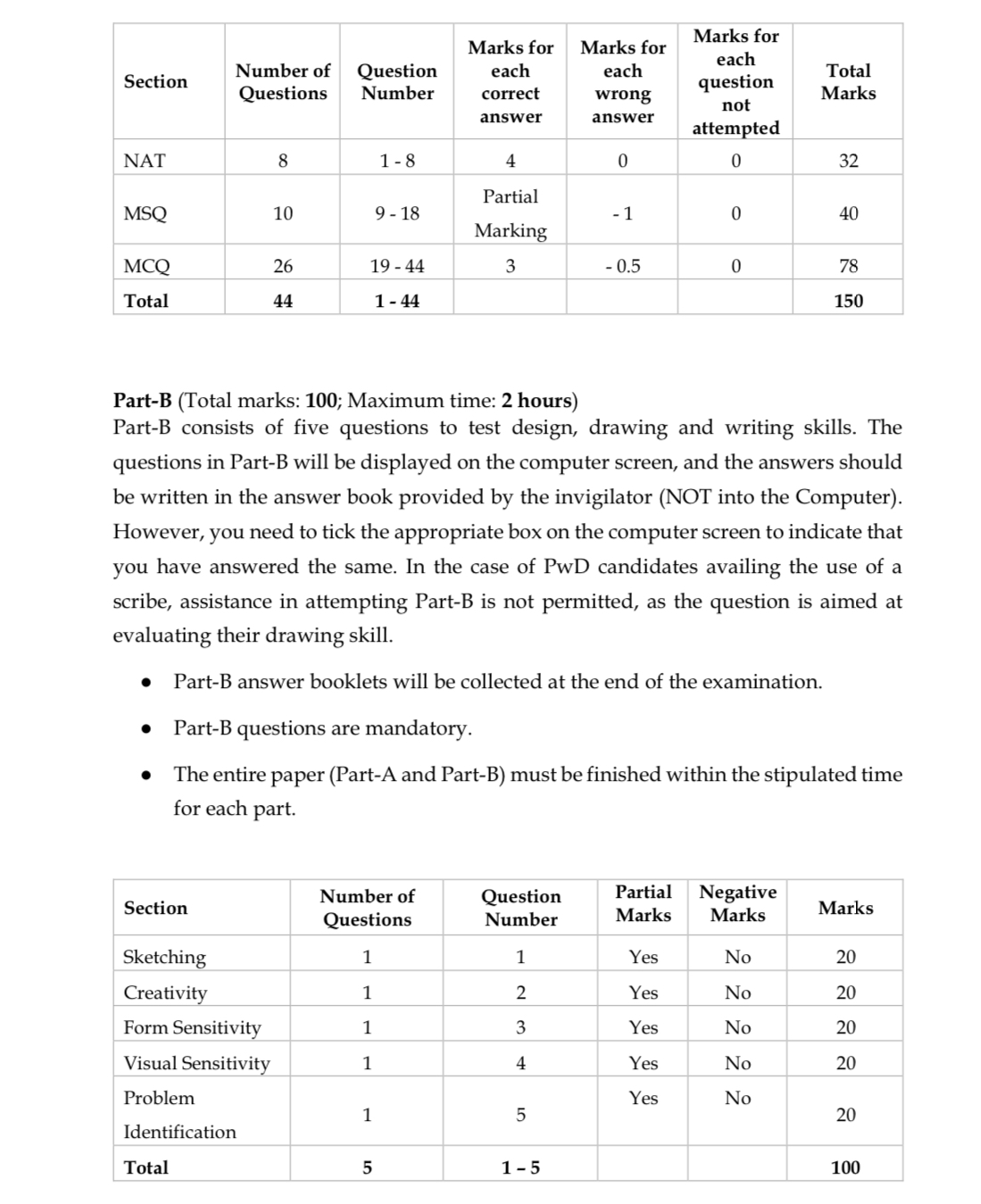
 The objective of the Common Entrance Exam for Design (CEED) is to assess the candidate’s aptitude for design involving visual perception ability, drawing skills, logical reasoning, creativity, communication, and problem solving skills. CEED is conducted by IIT Bombay. It is a qualifying examination for admission to Master of Design (MDes) programmes at IISc Bangalore, IIT Bombay, IIT Delhi, IIT Guwahati, IIT Hyderabad, IIT Jodhpur, IIT Kanpur, IIT Roorkee, IIITDM Jabalpur, IIITDM Kancheepuram and PhD programmes at several IITs and design schools. Qualifying in CEED alone does not guarantee admission to any of these programmes. Admitting institutes may conduct further tests and/or interviews for the final selection/admission.
The objective of the Common Entrance Exam for Design (CEED) is to assess the candidate’s aptitude for design involving visual perception ability, drawing skills, logical reasoning, creativity, communication, and problem solving skills. CEED is conducted by IIT Bombay. It is a qualifying examination for admission to Master of Design (MDes) programmes at IISc Bangalore, IIT Bombay, IIT Delhi, IIT Guwahati, IIT Hyderabad, IIT Jodhpur, IIT Kanpur, IIT Roorkee, IIITDM Jabalpur, IIITDM Kancheepuram and PhD programmes at several IITs and design schools. Qualifying in CEED alone does not guarantee admission to any of these programmes. Admitting institutes may conduct further tests and/or interviews for the final selection/admission.




 Pahal Design Bangalore Centre Offers Weekdays and Weekends batch for CEED Students. Weekends Batches are generally suitable for working Professionals or Final year appearing students. CEED Students Bangalore can also Join Classroom Coaching and Online Coaching. Pahal Design Bangalore Centre is at heart of city which is Indira Nagar.
Pahal Design Bangalore Centre Offers Weekdays and Weekends batch for CEED Students. Weekends Batches are generally suitable for working Professionals or Final year appearing students. CEED Students Bangalore can also Join Classroom Coaching and Online Coaching. Pahal Design Bangalore Centre is at heart of city which is Indira Nagar. EXAMINATION CITIES
EXAMINATION CITIES Partial Marks: + 1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it is a correct option and NONE of the incorrect options is chosen.
Partial Marks: + 1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it is a correct option and NONE of the incorrect options is chosen. Graphic designers create visual concepts, using computer software or by hand, to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, and captivate consumers. They develop the overall layout and production design for applications such as advertisements, brochures, magazines, and reports.
Graphic designers create visual concepts, using computer software or by hand, to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, and captivate consumers. They develop the overall layout and production design for applications such as advertisements, brochures, magazines, and reports.